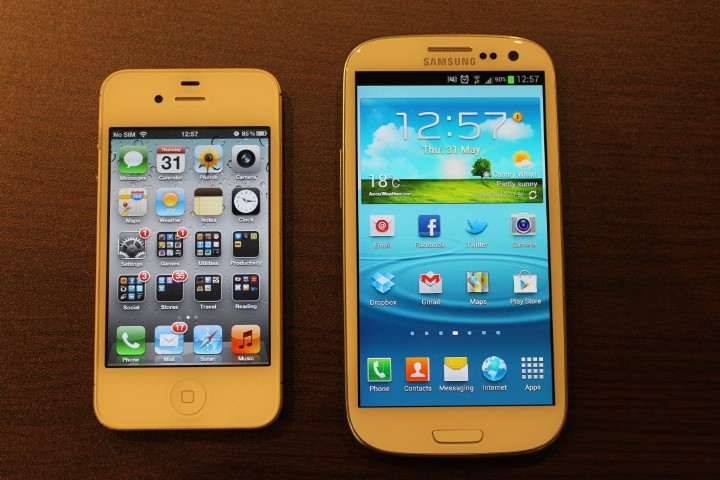
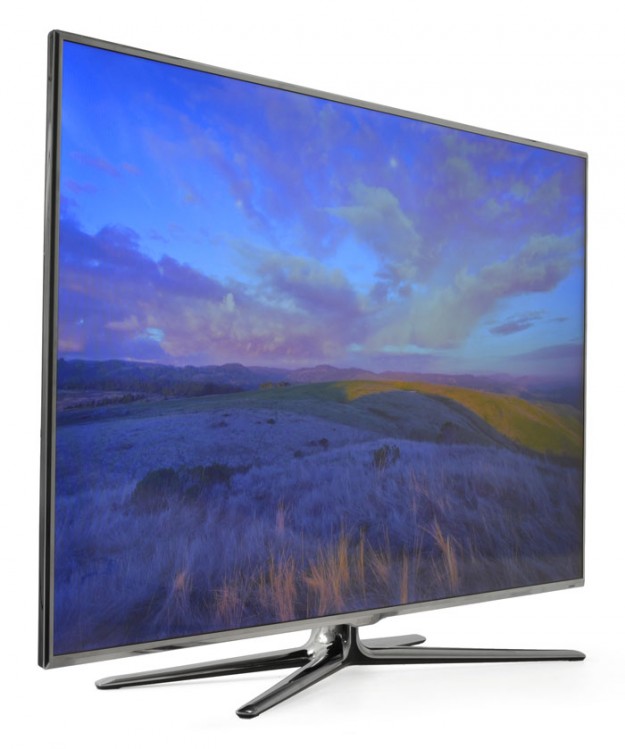
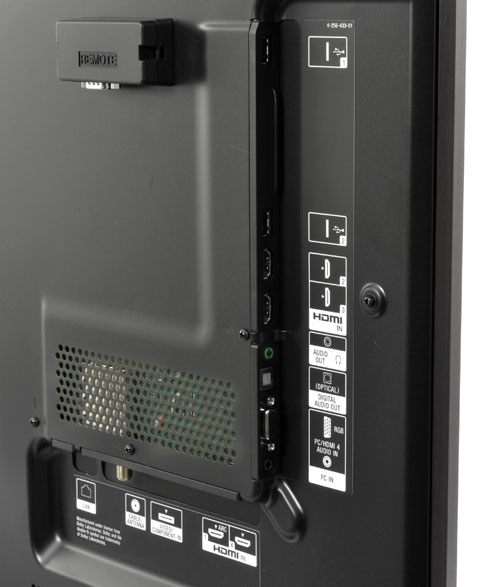
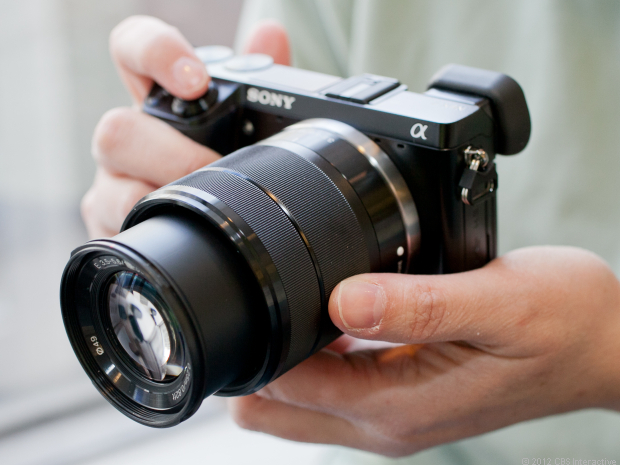
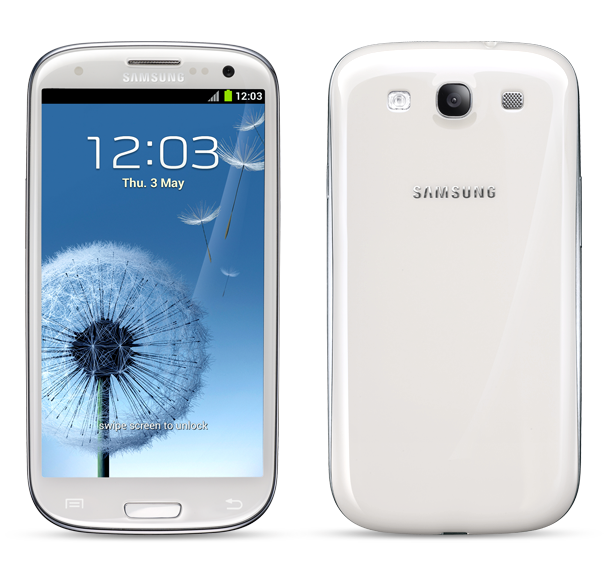
The Samsung Galaxy S3 has arguably become the most popular Android phone of 2012 – following in the footsteps of its highly successful predecessor, the Samsung Galaxy S2.
 If you’re looking for a smartphone with a really big screen and tons of features, the Samsung Galaxy S3 will give you top notch performance with so many sharing and media features, you’ll still be discovering new ones a year from now.
If you’re looking for a smartphone with a really big screen and tons of features, the Samsung Galaxy S3 will give you top notch performance with so many sharing and media features, you’ll still be discovering new ones a year from now.
The Galaxy S3 comes with an enormous 4.8 inch 720p resolution display and a mega-fast quad-core processor running the show behind the scenes. There’s a shiny new design to rave about as well, although with its rounded look and corners, some are regarding it as a bit old school.
The Samsung Galaxy S3 comes in both 16GB and 32GB microSD card storage options. You can, however, expand these on your own or wait for the 64GB Galaxy S3 to arrive later this year. International Samsung Galaxy S3 on all carriers that offer it are very similar, so we’ve compiled performance reports from a number of models we’ve reviewed to give our overall impression of this smartphone. So without further delay here’s our review on the 2012 Samsung Galaxy S3.
Why should I get the Samsung Galaxy S3?
The Samsung Galaxy S3 definitely falls under the “premium” smartphone category. But for those of you on a tight budget, there are certainly quite a few mid-range Android phones on the market that are great as well. The Samsung Galaxy S3 is a smartphone for those who are willing to pay a hefty price tag for an extremely powerful device. If you want HD video streaming, custom web surfing, 3D gaming, and high quality photo capture on a super powered processor with a massive display, then the Samsung Galaxy S3 is definitely a top contender.
Its chief competitor in the Android market would definitely have to be the HTC One X in my opinion, which is also the more affordable choice but not considered as powerful as the Samsung Galaxy S3. The “top rival” position though would definitely have to go to the Apple iPhone 4S, which comes in at roughly the same cost as the Galaxy S3. The iPhone’s iOS software is generally considered to have a simplified interface that’s easier to use than Android. But for those of you who love the freedom and control of that Android’s customization delivers to your digital environment, the Galaxy S3 would be the better choice.
Wi-Fi, Audio, and Call Quality
I was surprised to find that the default call quality was actually very good by today’s standard. Volume was definitely on the high end, with no noticeable distortion from loud inputs. Its speakerphone isn’t quite up to par however, great to use indoors or while driving, not so much in crowded public areas. The integrated microphone did a superb job of cancelling background noise, while Bluetooth headsets worked perfectly with the Samsung S Voice calling system.
Within the Galaxy S3’s call settings, a Volume Boost button bumps up the audio significantly for noisy areas, and a custom call EQ option allows you to customize audio call quality to your specific hearing.
The earpiece sounded crystal clear as well, with EQ customization available for it as well. No issues with its microphone either.
The Galaxy S3 supports Wi-Fi on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands in addition to Bluetooth 4.0.
Software and CPU Performance
The Samsung Galaxy S3 runs the Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich operating system. Up until just last month, Android 4.0 Ice Cream Sandwich was the most recent version of the Google operating system. Released in July 2012, Android 4.1 Jelly Bean will be officially available as an update to the Samsung Galaxy S3 sometime this fall.
Google’s Android is a very powerful, yet flexible operating system that leaves plenty of breathing room for user customization. Its biggest strength could also be its biggest weakness however, since a multitude of options and tools can be a little overwhelming for the casual newcomer.
In addition to Android, Samsung threw in its own software, TouchWiz. This is the same interface you’ll find on the Galaxy S2 and Galaxy Note. TouchWiz definitely looks great, but it sometimes loses favor in the ease-of-use department.
For example, in order to add a widget to the home screen position of your choice, you have to navigate into the apps view, switch to the widgets tab and then long press on the widget. Another example is the notifications interface. Even if you turn on SMS notifications in the settings, if the notifications icon is toggled off in the notifications tray, you won’t hear any sounds until it’s toggled on. It all works out once you see this icon, but if you haven’t, you’d be lost as to why you can’t hear when you receive an SMS.
Bottom line: Galaxy S2 users won’t have any trouble using the new S3 interface, but newcomers will have to dedicate more time getting used to it.
Design
All Samsung Galaxy S3 models look the same with the exception of different carrier logos engraved on the back panel. Color options include white, dark blue and red exclusively with AT&T. Measuring 5.4 by 2.8 by 0.34 inches and weighing in at 4.7 ounces, the Samsung Galaxy S3 is one of the biggest phones we’ve seen in a long time. It has a removable 2100mAh battery and a microSD card slot with storage support of up to 64GB.
For this model, Samsung went for a more oval-shaped look that resembles the Galaxy Nexus more than its rectangle-shaped predecessor, the Galaxy S2. The Samsung Galaxy S3’s corners are smoothed and rounded, while its curved back is lacking the rear-facing bumps present on both the Nexus and the S2.
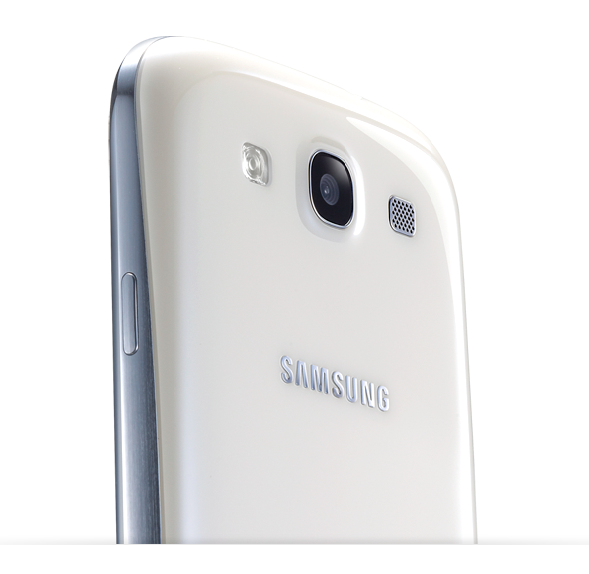
Its 8 MP camera is located on the back panel, which, thanks to a highly reflective finish, can double as a pocket mirror. (Just don’t expect to see that on the official Samsung Galaxy S3 features page).
Despite its size, the Galaxy S3 is surprisingly light in comparison to the Droid Razrs and the HTC one series. Nevertheless, the phone is incredibly well built, and light despite its size.
Below the front screen, there’s the physical touch Home button we’re all familiar with, as well as a light-up back button and multitasking button that start out invisible, so you have to memorize where they are or just change the settings to keep them constantly lit.
This button placement is somewhat inconvenient. We found ourselves accidentally triggering them with our hands once or twice because they’re so close to the edge of the phone.
The power button doesn’t stick out much on the curved right edge of the S3, so it’s a little inconvenient to use. The volume buttons on the left side of the phone however are big enough to use easily, and highly responsive.
The back of the Galaxy S3 has a high-gloss finish, so those of you with sweaty palm issues beware. The chrome trim also has a super-shiny coating so its sides are kind of slippery. These high-shine surfaces are compounded by all the gentle curves of the phone. Basically after a few days of use I found myself in line for a rubber grip case – which I would recommend you use on all smartphones anyway.
 The rounded corners are kind of retro for my taste, reminding me a bit of my Palm Treo 680 days. And yet, the Samsung Galaxy S3 still finds a way to still feel surprisingly modern to me with a luxurious feel. Even with its large screen, the S3 is very manageable. Sure you may have to stretch your hand out a bit to reach everything, but the advantage of having so much room to look at your photos, videos, and apps really make it a big plus in my book.
The rounded corners are kind of retro for my taste, reminding me a bit of my Palm Treo 680 days. And yet, the Samsung Galaxy S3 still finds a way to still feel surprisingly modern to me with a luxurious feel. Even with its large screen, the S3 is very manageable. Sure you may have to stretch your hand out a bit to reach everything, but the advantage of having so much room to look at your photos, videos, and apps really make it a big plus in my book.
Overall built quality has been all around strong for the Samsung line smartphones, and the Galaxy S3 is no exception. Despite being made predominately of a glossy plastic casing, it feels reassuringly stuck together. The screen is rock solid and the generous chrome trimming keeps everything in line. I wouldn’t recommend risking a drop however – as I’ve already seen an S3 with a cracked screen after taking an accidental fall.
 You can make the S3 faintly creak by squeezing it tightly from the sides. But taking into account that it has a removable backplate for battery, micro SD and micro SIM slots, it’s not surprising. But overall, the design quality of the Samsung Galaxy S3 has a premium look and feel.
You can make the S3 faintly creak by squeezing it tightly from the sides. But taking into account that it has a removable backplate for battery, micro SD and micro SIM slots, it’s not surprising. But overall, the design quality of the Samsung Galaxy S3 has a premium look and feel.
Screen
The front of the Samsung Galaxy S3 is almost completely taken up by its 4.8 inch, 1280 by 720 pixel Super AMOLED High Definition screen. It’s a PenTile screen, which can sometimes look a little by pixilated, and it’s a bit dimmer than other well known premium smartphones. But you can always turn off the auto-brightness however, which will eliminate the dimness effect. PenTile screen technology is well received for many reasons actually, but mostly because of its low power consumption as compared to simple RGB stripe displays, and its ability to achieve an HD resolution on an AMOLED screen.
The Samsung Galaxy S3 display measures an impressive 4.8 inches on the diagonal which makes it one of the largest smartphones currently on the market. But while you may find your thumbs stretching in new and interesting ways, the main benefit here is that a larger display makes your video, pictures and games look absolutely marvelous.
This is a full HD Super AMOLED screen, which is the same display technology implemented on the Nexus and Note, both of which are also eye candy. AMOLED screens offer vibrant colors and extremely deep blacks. The only downside is that, unlike the Samsung Galaxy S2, the S3 is does not have a Super AMOLED Plus display. That translates to fewer sub-pixels per pixel than the S2’s screen. Some of you might but a little discouraged at this fact, but I sincerely doubt the majority of you will even notice a difference.
Another letdown for me was how the Galaxy S3 performed under direct sunlight. To be honest I was hardly surprised considering not many smartphones do well under the sun anyway, but I had to really struggle to see the S3’s screen during the hours of noon to 3pm, with content ghostly and indistinct and a reflective blue sheen masking what’s on the screen. I spent most of my time sitting at a desk so it’s not a huge issue for me, but if you do need to use your phone outdoors a lot, there are quite a few smartphones that are designed with outdoor viewing in mind.
The Samsung Galaxy S3 pixel density per inch is actually not the sharpest currently on the market. At 306ppi it’s not quite as high resolution as the Sony Xperia at 342ppi, the HTC One X at 312ppi, or the iPhone 4 and 4S at 326ppi. But it is still an impressive screen nonetheless. The general consumer probably won’t notice much difference between all of these displays at all.
Camera
The Samsung Galaxy S3 comes with an 8 MP camera, which is no improvement in resolution from last year’s Galaxy S2. It may not have improved in pixel count, but the S3 does have a few extra features, including the zero shutter lag found also in the Galaxy Nexus, and a cool feature that automatically suggest your best shot after you’ve made a few similar captures, basing its decision on factors like smile detection and face recognition. Another new addon that I really loved, also present on the HTC One X, is the ability to take still images while you’re recording video.
The Samsung Galaxy S3 Camera was definitely impressive, producing professional quality close-up shots, both indoors and out, and having a really good shallow depth of field. Overall, its colors are true to life, with the exception of some slight over saturations on some shades.
It’s also really good at dealing with the lower light of an indoor environment, but it does have some very slight issues with variable light conditions across one scene. I found it would wash out parts of the scene, while also suffering from the occasional lens flare.
The Samsung Galaxy S3 camera fairs pretty well against other premium smartphones, beating out the Sony Xperia S, but not quite up to par with the iPhone, HTC One X, or the Nokia 808 PureView.
The Galaxy S3 also shoots full HD video at 1080p resolution. Video results during testing tests were less impressive than camera shots, with a tendency to look a little hazy at times. Levels of detail also change with slight movement of the frame, such as during walking. There is also a 2 MP camera located on the front for video calling, Face Unlock and Samsung’s face detection feature, which stops the phone’s screen from dimming as long as you’re looking at it.
Contacts and Messaging
The Samsung Galaxy S3 contacts application includes some cool new features. When you swipe left over a contact’s name, it will take you straight to the messaging menu so you can send an SMS very easily. If you swipe to the right of a name, it will automatically call the contact without you having to tap twice.
You can create groups or lists of contacts so you can quickly sent emails or SMS to multiple people at one time. If you’re trying to find a contact in your address book, you can press on the corresponding letter of the alphabet in the index at the right hand side to jump down to the right section, or you can also just start typing their name into the search box. The software favors last names over first so make sure you remember that!
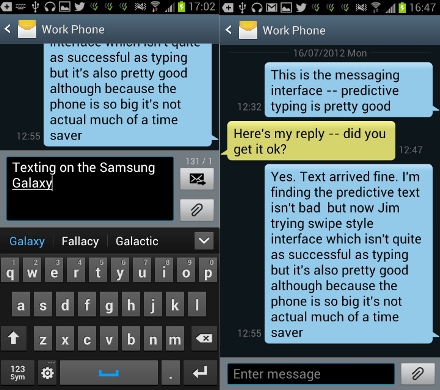
The basic messaging interface of the S3 is clean and very easy to use. It displays a speech bubble graphic to show conversation threads. If you’re composing a text in landscape mode you won’t be able to see the preceding messages in the thread, but in portrait mode you can scroll back through to read them if you want. The well known “Swype” style interface is preloaded on the Galaxy S3, which can be switched on, if you turn on the continuous input within the Samsung keyboard settings.
Eye tracking
A cool new feature on TouchWiz is Samsung’s eye tracking technology. This uses the Galaxy S3’s front view camera so it can keep the screen on if it detects a face looking at it. It’s a really cool addon that works great if you’re holding the phone directly in front of your face. But if for any reason you’re looking at it from an angle, (maybe you’re resting your head on a pillow or something), it won’t register your face and will turn off anyway. The flashing eye symbol is also a bit distracting, delivering a constant, eerie reminder that your S3 is watching you.
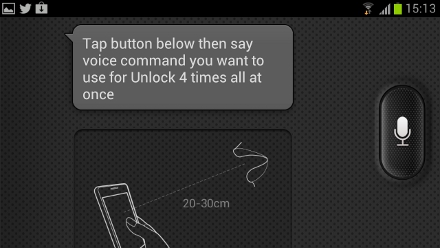
Face and Voice Unlock
Using the S Voice feature I’ll mention talk about a bit later, The Samsung Galaxy S3 allows you to set a facial and voice recognition code before it unlocks the phone. It’s pretty straightforward to set up, but I can’t imagine many people wanting to talk to their phone every time in order to unlock it.
Web browsing
On this high resolution display with the S3’s powerful processor, it’s almost a given that this phone would have excellent web browsing. Websites are very quick to render (depending on your cellular network of course) and look absolutely gorgeous on this larger display. Still no support for Adobe Flash however, so some embedded video and other content won’t display.
The S3 scored 1,498.9ms on the SunSpider JavaScript benchmark test, which evaluates a browser’s speed — beating the iPhone 4S’s score of 2,181.6ms by a considerable margin, and more than halving the Samsung Galaxy S2′s 3,445.3ms. Lower is better in this test as it’s a measure of time taken.
The S3 even trumps the new iPad in this test. Apple’s newest tablet scored 1,890.9 when we benchmarked it, while the iPad 2 was about the same at 1,884.6 — both taking slightly longer than the S3.
Apps
One cool little thing to mention first within the Apps section is that the Samsung Galaxy S3 comes with two years of included online storage for Dropbox, giving you 50GB worth of memory to dump all of your files and media in.
The former Apple exclusive app, Flipboard, comes with the Galaxy S3 and turns updates from your favorite social networks, websites, and blogs into a clean, magazine-style layout. The Galaxy S3 also comes with a lot of preloaded Samsung apps, several of which, including S Suggest and Games Hub, give you additional ways to get content on your phone, as well as being able to download apps from the Google Play Store.
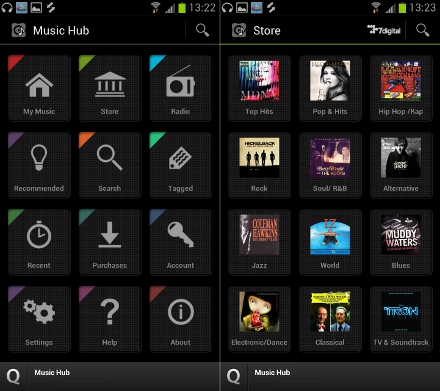
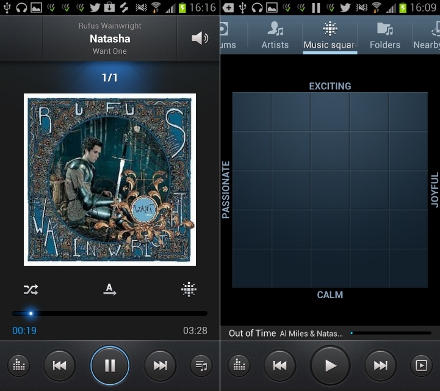
Music
Samsung’s Music Hub app makes an appearance on the Galaxy S3, which links through to a 7 Digital-powered music store where you can listen to clips and download songs right on your phone.
Purchasing songs is a fairly simple task, organized similarly to Apple’s iTunes.
Once you’ve download all your favorite music you can play them using the Samsung Music Player.
This includes the Music Square feature, which designs custom playlists based on the music your listen to.
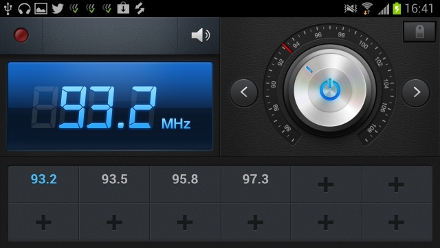
In addition to Music Player, Samsung had the FM Radio app which comes with an analogue-style knob interface and the ability to save station presets so you can easily come back to them with a single tap. From this app you can also record content from the radio station you’re listening to.
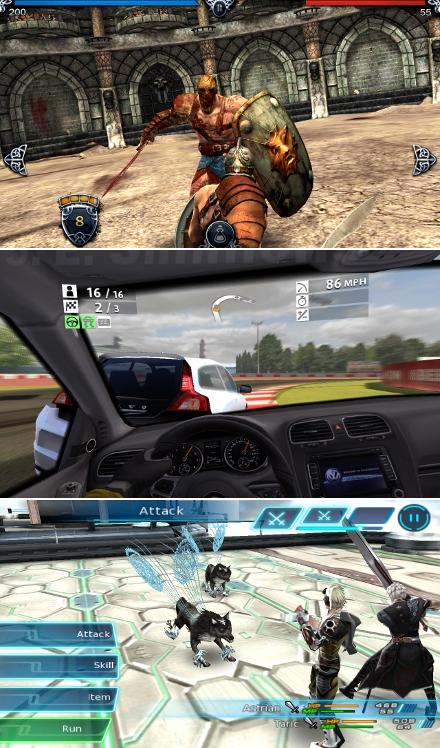
Gaming
With its 1.4GHz quad-core processor, the Samsung Galaxy S3 is more than capable of delivering high resolution video and graphically demanding 3D games. Its performance feels smooth with little to no lag on some of the heavier graphics games.
Well, I guess what I’m saying is it will be very difficult to find a game on Google Play that will stretch a processor to its limits. Gameplay overall its smooth, with no noticeable slow down.
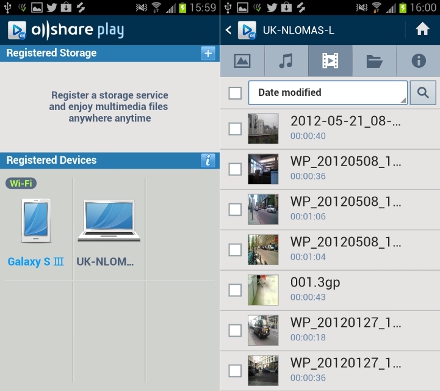
AllSharePlay
AllSharePlay is a Samsung feature that creates a network for your content stored on multiple devices so you can easily access it from your Galaxy S3. Think of it as the “cloud”. To set it up all you need is a Samsung accounts and then download the AllSharePlay software to the devices where you want to access your data from, such as a laptop or tablet.
After you’ve installed the program and logged in, you be able to locate your files when launch AllSharePlay on your Samsung Galaxy S3. In addition to viewing your content, you will also be able to download files locally on your Samsung Galaxy S3 through the app as well. That means you can access your files and download them even when you don’t have a Wi-Fi connection.
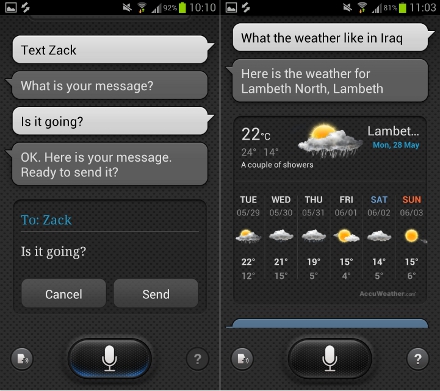
S Voice
S Voice is a voice control assistant application that resembles Apple’s Siri. Just like the iPhone feature, S Voice has a “tap to talk” microphone icon interface that can perform task like making a call, setting an alarm, giving you the weather, controlling music playback or taking a picture. For the most part though, just like Siri, I had to repeat what I wanted a couple of times and even then I wasn’t guaranteed a right answer. Most of the time I think it’s just quicker to navigate to the feature you want on your phone manually then through voice control.
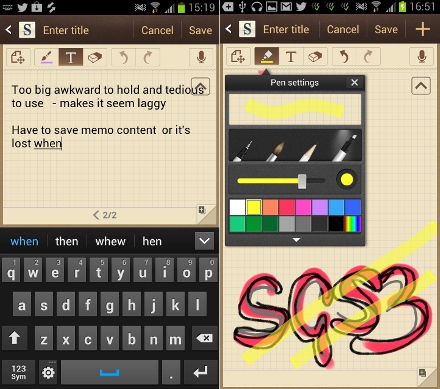
S Memo
This Samsung feature allows you to design both text or scribble hand drawn notes. It’s has more options than Apple’s Notes app, with a range of pens and colors to pick from, as well as its ability to allow hand written notes, not just typed text. You can also attach photos to memos, encrypt your private memos and add an audio recording too – pretty handy if you like to record a meeting, seminar or lecture as you take notes.
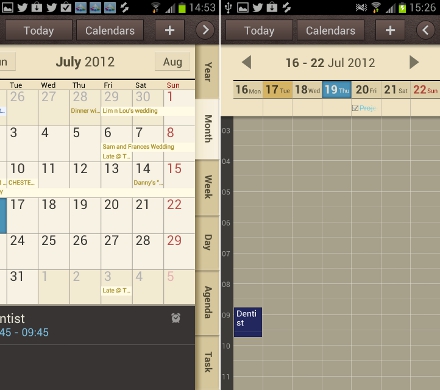
S Planner
This is the Samsung Galaxy S3 calendar app that comes with some cool features. For example, you can pinch to quickly zoom in and out from day view, to week, to month and to year. S Planner can also directly synchronize with Google Calendar. Among other you can set reminders, add event participants, and link the app with S Memo, so you can attach notes along with your calendar appointments.
Battery Performance
The Samsung Galaxy S3 comes with a removable 2100mAh battery. A full brightness, the S3 will run through your battery life fairly quickly, so keep an eye on your battery icon at the top corner of the screen. Ideally on any smartphone, you should avoid full brightness for long periods of time.
With the display set to 50 percent brightness, the S3 battery dropped from 100 percent to 60 percent just after around 4 hours of streaming HD video over a Wi-Fi connection. By comparison, the HTC One X went down to 30 percent battery in the same test. So assuming that you don’t crank up the screen brightness all the way, you should be able to get 6 to 7 hours of video streaming on a single charge.
Expect to have to charge your phone every single night – perhaps even sooner if you’re a smartphone junky like me. Something interesting to note is that the Galaxy S3 charges a lot slower over a USB connection. So if you need a lot more power on a quick charge, I’d suggest hooking it up to a wall socket.
Samsung also included a “power saver mode” feature that automatically limits CPU performance, dims the screen, change the background color in web browsing and turns off haptic feedback (tactile vibrations).
But, you could argue that the whole point of getting the phone in the first place is to take advantage of these features, which then brings us to the question of whether a quad core processor isn’t overkill for a smartphone. But the Samsung S3’s performance does make it quite fun to use.
Final Verdict
With applications downloading and launching super quick, HD video playing smoothly and menus and gallery photos reacting simultaneously to your finger gestures, the Samsung Galaxy S3 has certainly proven itself as one of the top smartphones of 2012.